It’s an exciting time in 3D printing—both in the classroom and in the industrial world. Much of the excitement and innovation being applied in the classroom has been developed by leading tech companies and tweaked to gel with modern education. Want to learn about the different 3D printing technologies, how they work and why robots might soon have a role in 3D printing?
The Different 3D Printing Technologies and How They Work
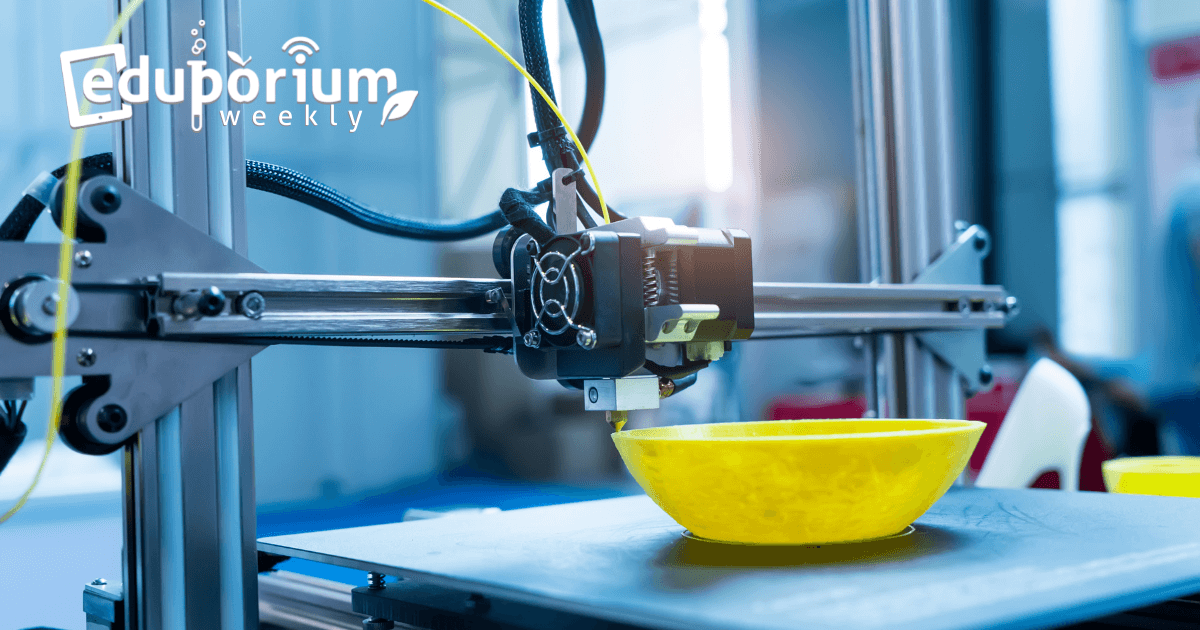
You may be mildly familiar with 3D printing and its practical uses in today’s hands-on world as well as in tech-focused STEAM classrooms. You may not know, however, just how far 3D printing innovation spans and the amount of super cool technologies that enable and enhance 3D printing. While still essentially in its infancy, 3D printing technology is developing rapidly and now includes desktop printers, large-scale machinery and even laser cutters. While it certainly has the potential to be the next big thing in STEM education, it is pretty huge already. In fact, many 3D printers have been designed and created specifically for use in today’s K-12 schools and classrooms!
In 3D printing, materials that include plastic, metal, ceramics or even other textures are printed layer by layer until the final product reveals a tangible object. While there are a few different methods of 3D printing, each one of them is executed with the help of a computer program and computer aided design (CAD) files. These files are very important to the printing process as they instruct the printer how the objects being put together are to be layered. Many of these files are open source, meaning they can be shared and distributed online and used with almost any 3D printer. For those who get really good at it and would like to optimize their designs or add customization, they may need to use specialized software, but you can worry about that later on!
Though 3D printing involves a number of different technologies, the basic idea remains the same in most cases. Like many of today’s technology, some 3D printing tech will soon become extinct, some will be available for home use and some will be able to be used for enhancing the completion of specialized tasks. The most popular method of 3D printing is called Fuse Deposition Modelling or FDM. Using polylactic acid or acrylonitrile butadiene styrene plastics as raw materials, hot plastic flows out of the nozzle to create layers with each new layer bonding to the previous one. This is the ideal method for 3D printing projects in an educational setting. There is also Selective Laser Sintering, Polyjet Printing, Stereo Lithography and Digital Light Processing to round out some of the techniques used by scientists and makers to create tangible objects out of digital designs.
Why 3D Printing is on its Way to Classrooms
As educators continue to embrace making in the classroom, students are constantly seeking new and innovative ways to personalize complex projects. Technology and maker education are becoming a huge part of the 21st century learning experience as they allow for increased creativity and carve new, ingenious avenues for students to explore. When it comes to 3D printing, kids are empowered by innovations in hands-on technology and are able to push their creative potential to the limits. The Maker Movement and, in particular 3D printing, has encouraged today’s students to take their learning into their own hands and contemporary tools have truly begun to use design, tinkering and building as a way of solving problems and shaping skills.
Because of its potential for innovation as well as its real-world relationship, 3D printing is becoming a fixture in many elementary, middle and high schools as education programs look to shift the focus to preparing their students for a hands-on world. There are more advantages to having 3D printing in education, however, than just preparing students for the future. For students, 3D printing provides a tangible framework for trial and error as it requires that they take their ideas through a production process that includes digital design, testing and analysis. It also helps create a connection between a problem and an innovative solution. Many of today’s 3D printing enthusiasts embody a true sense of community, meaning that they are constantly sharing and listening to ideas published on the Internet. Students can use their 3D printing skills to help create devices that real people need to improve their lives, but cannot procure on their own.
To put it simply, 3D printing in education may not be special for long—it could very easily become ordinary. One reason for this is that it helps demystify engineering and assists in illuminating concepts that students have come to believe are much too complex in simple and straightforward ways. During the actual project process, 3D printing offers flexibility in design as the filaments used can lead to final products that are any number of shapes or sizes. A lot of the time, 3D printing is used when a small part of a device breaks so that the entire thing does not have to be replaced or it can be used to create customized equipment for kids or adults to improve their everyday lives. Finally, 3D printing is not a bank-breaking endeavor. Many 3D printers are completely affordable and a lot are even designed and priced specifically to break into STEM classrooms!
3D Printing Can Transform the Way You Teach
Besides its real-world ramifications, 3D printing has a whole other layer of upside when used in today’s classrooms. If you’re not sure what to expect or not sure how to use a 3D printer, don’t worry—you are not alone. Thankfully, 3D printing technology has become quite intuitive in this day and age and because of this and affordability, they have made a sizable splash in the education world. It may take some time to get familiar with the technology, engage students or convince administrators that 3D printing is worth the time and money, but once you do, you and your students will reap the rewards for years to come—and here’s how!
At any grade level, 3D printing facilitates deeply meaningful learning, meaning that student satisfaction is maximized when they can physically hold something they put their mind to creating. It changes how they view and understand the world. In fact, 3D printing isn’t just for science subjects—it can be used to create projects and real-world solutions for any grade level and in almost any class in the curriculum. The concepts that 3D printing helps hammer home are regularly used in the contemporary world and, most of the time, curious students strike up deeper conversations among their in-class groups centered on anything from design suggestions to future applications of the products they have printed, leading to enhanced critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
When students take pride in their work and strive for an outcome that legitimately benefits them or somebody else, they become engaged with the subject matter or a personal level and 3D printers are ideal for personalizing tech-focused lessons. Since engagement is amplified, projects that make use of 3D printers tend to compel kids to think big. They can literally leave their legacy behind by creating physical objects with technology. More importantly, 3D printing also teaches students that it’s more than okay to fail—as long as they learn something and apply what they have learned to improving their project the second time through. And, most importantly, kids can begin developing their creative design skills to fashion devices that genuinely help friends, strangers or the general community all while taking complete control of their STEM education!
3D Printing Trends Around the World
It’s true that 3D printing did get its start in the manufacturing industry and it took a bit of time for it to penetrate modern-day education, makerspaces and even the homes of hobbyists. Almost every month the popularity of 3D printers seems to be rising around the world, however, resulting in the number of machines that sold to increase with it. Manufacturers of 3D printers are constantly updating their products, which leads to new and improved devices all the time. This also enhances competition among manufacturers and ensures that the people who want to use 3D printers often have some of the latest and most efficient technology with which to work.
This constant change and competition opens the door for new companies to get into the 3D printing game on a regular basis. Two manufacturers in particular have recently taken advantage of designing printers that correlate with exactly what consumers are looking for. Ultimaker has created a line of printers that not only enhance STEM education but maker education as well. What do we mean? Along with printers of various sizes (from mini to plus-sized), the Ultimaker Original is a 3D printer that children can construct themselves. Another emerging brand is XYZ, who has created printers of various shapes and strengths while remaining incredibly affordable. The standalone technology found in XYZ 3D printers offers kids, in particular, a safer and more efficient 3D printing experience.
When it comes to the most popular 3D printing cities in the world, the US is well represented with five of the top-10 3D printing cities located in the country. New York and Los Angeles are the top-2 3D printing hubs worldwide, according to a recent report, while Chicago checks in at No. 7, San Francisco landed at No. 9 and Seattle squeaked in at No. 10 overall. This should come as no surprise as 3D printing, especially in education, has undergone a tremendous spike in popularity over the last few years. Some of the other cities where 3D printing is huge include London at No. 3, Milan at No. 4, Paris at No. 5, Amsterdam at No. 6 and Toronto at No. 8. From what experts have gathered, this surge is due, in large part, to most of the 3D printers sold nowadays using PLA filament, which provides for a much smoother printing experience and helps students break into a future of hands-on learning earlier than ever!
Could More Than 3D Printers 3D Print Things?
What if we told you that 3D printers might not always be the only tools that people can 3D print things with? Or at least, 3D printers in the traditional way that we think about them. Sure, the advances in technology will probably continue to be created, but one recent idea, which seems entirely plausible, caught our attention. A couple of months ago, engineers from Siemens designed and completed prototypes of a 3D-printing spider robot. I guess eight legs are better than one as apparently these fairly small machines could be used to 3D print anything from an entire car to an airplane fuselage. Now, that’s cool.
Besides it being completely awesome, innovation of this degree would be very beneficial to modern companies. It would help cut labor costs and save tons of time on production and construction. And, oh yeah—these 3D printing robots are portable, making them one of the first attempts at launching mobile manufacturing and indicating just how far technology advances have come. Siemens’ robots will likely allow engineers and artists to construct and manipulate objects in places they were previously unable to physically reach. Given the rise of robotic automation across a lot of the world’s industries, this kind of model could be just the start of a very powerful trend.
Each machine works in tandem with the other machines in the group according to the specific way they’re each programmed. They appear to have eyes, but those are actually laser scanners, which read the robots’ surroundings and communicate with its extruder arms to let it know exactly where to build. The software in the robots allows them to each work on a specific area without getting in each other’s way. While scientists don’t know right now how long it would take to construct a car or a fuselage or how many robots they would need, it certainly is an exciting time in 3D printing. Just think—soon there could be little tiny 3D printers running around, creating some of the most important tools we need to function from day to day.
For the latest EdTech, STEM, and 21st century education news, follow us on Twitter and Instagram. Like us on Facebook, too, or sign up for our newsletter for our latest product announcements and offerings. If you have an idea for an Eduporium Weekly theme, send us a message on social media or comment below.



1 Comment